
This ledger provides details such as the date, amount owed, and the supplier involved. Understanding these differences helps maintain accurate financial records and aids in making informed business decisions. In the general journal you must enter the account(s) to be debited and the account(s) to be credited along with their amounts and a brief description.
- Ledgers play a crucial role in preparing proper financial statements, since they gather together the data that will be required to determine account balances.
- This section allows us to understand how the journal serves as a raw transaction book and why it’s so important in constructing a financial story for a business.
- However, it should be noted and due to rise in bookkeeping software, the use of journals and ledgers are decreasing.
- These articles and related content is the property of The Sage Group plc or its contractors or its licensors (“Sage”).
- It keeps the balance sheet balanced by debiting one account and crediting another.
What is a chart of accounts, and how does it relate to journals and ledgers?
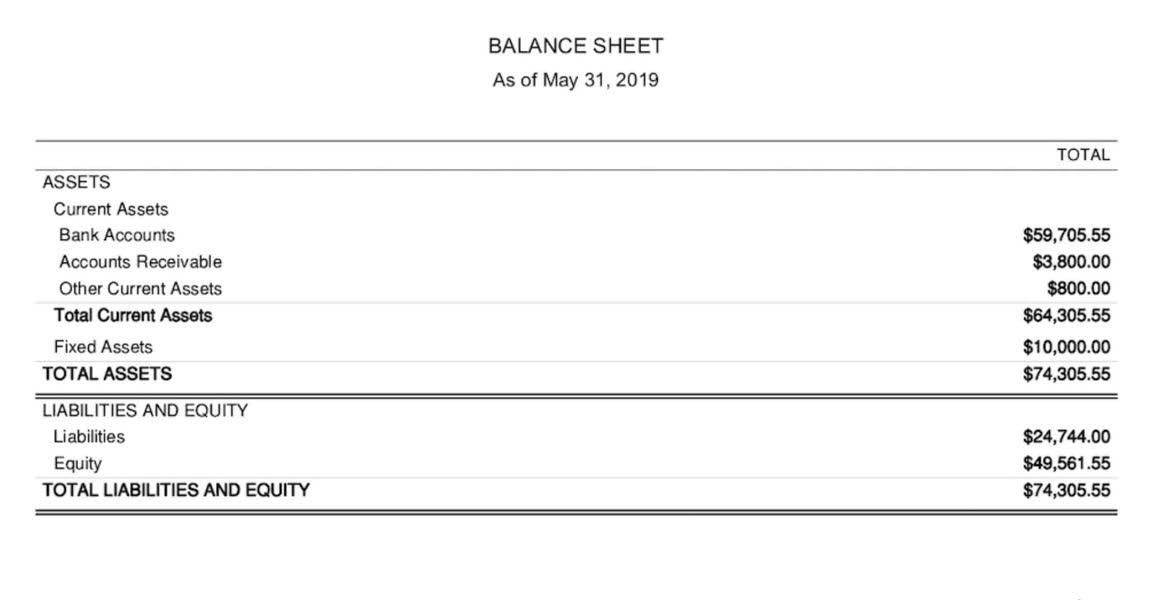
This includes generating income, maintaining operations, and achieving financial objectives. Turning a transaction into a financial statement takes careful record-keeping. The general journal vs general ledger discussion is not just theoretical. Knowing the difference is crucial for finance students and professionals. When a transaction has more than one debit or credit entry or both in a single entry, it is called a compound entry. A compound journal entry is a type of accounting entry where two or more transactions are recorded together in a single journal entry.
Why are Journal and Ledger Important in Bookkeeping?

It serves as a detailed and comprehensive account of all transactions, including the date, description, and amount. On the other hand, the ledger is a summarized version of the journal, where transactions are classified and grouped into specific accounts. It provides a clear and organized overview of the financial position of a business, as it contains separate accounts for assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. While the journal Financial Forecasting For Startups captures every transaction, the ledger presents a more concise and structured representation of the company’s financial activities. Ledger of each account is maintained in ‘T’ format – with debits on the left and credits on the right. Once all journal entries are posted to their individual ledger accounts, they are balanced and the balances are compiled in the form of a trial balance.
Difference between Journal and Ledger – Journal Vs Ledger
Journals record transactions in order, laying the groundwork for financial records. This is crucial for history, IRS reviews, and audits by groups like the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. Ledgers then difference between journal and ledger organize these details, showing a business’s current financial health. It brings together info from journal entries into organized accounts. Each ledger account is for a specific accounting item like assets or expenses. This organizes transactions into summaries, crucial for financial reporting.

Accounting Basics
In a smaller organization, users may believe that all of their business transactions are being recorded in the general ledger, with no storage of information in a journal. Companies with massive transaction volume may still use systems that require the segregation of information into journals. Thus, the concepts are somewhat muddied in a computerized environment, but still hold true in a manual bookkeeping environment. Detail-level information for individual transactions is stored in one of several possible journals, while the information in the journals is then summarized and transferred (or posted) to a ledger. The posting process may take place quite frequently, or unearned revenue could be as infrequent as the end of each reporting period.
Whether transactions are entered via computer or handwritten, adequate record-keeping is a necessity to maintain accurate financial data and create your company’s financial statements. A General Ledger organizes transactions by account type, providing a structured view of financial data. It categorizes entries into assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses, whereas a General Journal records transactions chronologically without categorization. Journals act as the initial repository for recording transactions in accounting. Every financial event is documented here as it occurs, using the double-entry bookkeeping method to ensure debit-credit consistency.

- The ledger contains the chart of accounts, which is the list of all names and account numbers in the ledger.
- Understanding the roles of the general ledger and general journal is foundational to the efficiency of accounting processes.
- However, if you’re still using a manual accounting system, or using Microsoft Excel, you’ll need to record those transactions in a general journal.
- These records provide the foundation for creating accurate ledgers and financial statements.
- A ledger includes all the details such as revenues and expenses, liabilities, accounts for assets and the owners’ equity.
- The use of both journals and ledgers also makes accessing and analyzing financial records more efficient.
The journal is the original document, and all other financial documents (ledger, bank statement, etc.) are derived from it. As such, the journal should be kept in a safe place and updated on a regular basis. Ledgers may be kept for record-keeping purposes, but their primary benefit is that they can be used to generate financial statements (i.e., balance sheet and income statement).
